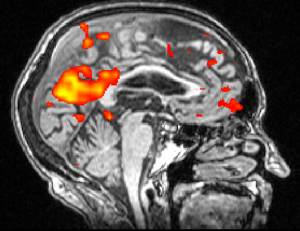
Mood Disorders
fMRI is especially useful in differentiating mood disorders that share common symptoms and has even been successful in categorizing depression into 4 separate sub-types. Each mood disorder can be seen as a unique signature in the brain, and through these signatures we can begin to understand the deeper mechanisms driving these disorders.
Treatments for Mood Disorders
While various pharmacological medications combined with psychotherapy have traditionally been used with some degree of success, many patients have turned to non-addictive treatment methods such as repetitive TMS (rTMS). Our physicians provide fMRI data specifically tailored for rTMS providers. These providers can then treat the activated areas of the brain visualized in the fMRI.
Sources:
1. Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Greicius MD, Flores BH, Menon V, Glover GH, Solvason HB, Kenna H, Reiss AL, Schatzberg AF; Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Sep 1;62(5):429-37. Epub 2007 Jan 8.
2. Resting-state connectivity biomarkers define neurophysiological subtypes of depression. Drysdale AT, Grosenick L, Downar J, Dunlop K, Mansouri F, Meng Y, Fetcho RN, Zebley B, Oathes DJ, Etkin A, Schatzberg AF, Sudheimer K, Keller J, Mayberg HS, Gunning FM, Alexopoulos GS, Fox MD, Pascual-Leone A, Voss HU, Casey BJ, Dubin MJ, Liston C; Nat Med. 2017 Jan;23(1):28-38. doi: 10.1038/nm.4246. Epub 2016 Dec 5.
3. Efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation targets for depression is related to intrinsic functional connectivity with the subgenual cingulate. Fox MD, Buckner RL, White MP, Greicius MD, Pascual-Leone A.; Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Oct 1;72(7):595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.04.028. Epub 2012 Jun 1.
4. Resting-state functional connectivity abnormalities in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder and their healthy first-degree relatives. Hou JM, Zhao M, Zhang W, Song LH, Wu WJ, Wang J, Zhou DQ, Xie B, He M, Guo JW, Qu W, Li HT.; J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014 Sep;39(5):304-11.
5. A systematic review of the neural bases of psychotherapy for anxiety and related disorders. Samantha J. Brooks, PhD, Dan J. Stein, PhD; Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2015 Sep; 17(3): 261–279.
6. Predicting Treatment Outcome in PTSD: A Longitudinal Functional MRI Study on Trauma-Unrelated Emotional Processing. Sanne J H van Rooij, Mitzy Kennis, Matthijs Vink & Elbert Geuze; Neuropsychopharmacology volume 41, pages 1156–1165 (2016) doi:10.1038/npp.2015.257.
7. Changes in brain connectivity related to the treatment of depression measured through fMRI: a systematic review. Gudayol-Ferré E, Peró-Cebollero M, González-Garrido AA, Guàrdia-Olmos J; Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Nov 3;9:582. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00582. eCollection 2015.
8. Combining TMS and fMRI: From ‘virtual lesions’ to functional-network accounts of cognition. Christian C. Ruff, Jon Driver, Sven Bestmann; Cortex. 2009 Oct; 45(9): 1043–1049. Published online 2008 Dec 6. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2008.10.012.